Causes, Symptoms & Effective Treatments
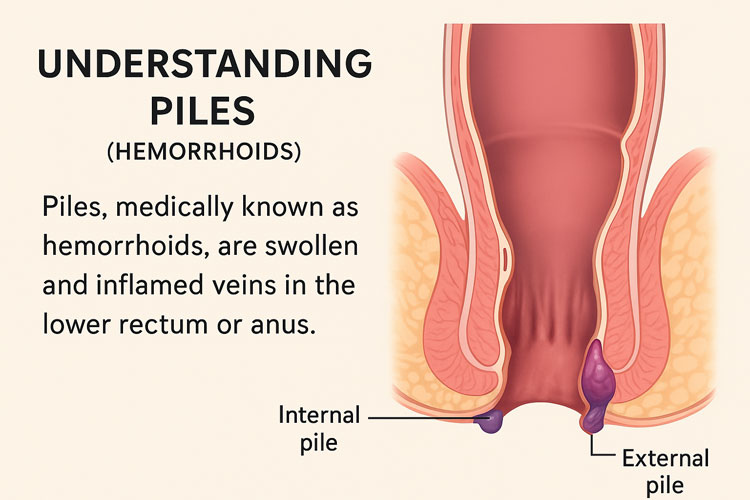
Piles, medically known as hemorrhoids, are swollen and inflamed veins in the lower rectum or anus. It is one of the most common anorectal conditions, affecting millions of people across all age groups. While piles can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful, they are easily treatable with timely care and lifestyle modifications.
What Are Piles?
Piles occur when the blood vessels around the anus become enlarged due to excessive pressure. They may develop inside the rectum (internal piles) or around the anal opening (external piles).
Types of Piles
- Internal Piles – Found inside the rectum and usually painless but may bleed.
- External Piles – Located under the skin around the anus and often painful.
- Prolapsed Piles – Internal hemorrhoids that protrude outside the anus.
- Thrombosed Piles – External piles that develop a blood clot, causing severe pain and swelling.
Common Causes of Piles
Several factors increase pressure in the pelvic or rectal area, leading to piles:
- Chronic constipation or hard stools
- Straining during bowel movements
- Low-fiber diet
- Long sitting hours
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Heavy lifting
- Aging and weak rectal tissues
- Hereditary tendency
Symptoms of Piles
The symptoms depend on the type and severity of hemorrhoids. Common signs include:
- Bright red bleeding during bowel movements
- Pain or discomfort around the anus
- Itching or irritation
- Lump or swelling near the anal area
- Mucus discharge
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation
If you experience persistent bleeding or severe pain, it’s important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.
How Piles are Diagnosed A specialist may perform:
- Physical examination
- Digital rectal exam
- Proctoscopy or anoscopy to inspect internal piles
- Colonoscopy (only if required)
- These tests help assess the grade and type of hemorrhoids.
Treatment Options:
Treatment varies depending on the severity:
1. Home Remedies:
- Increase fiber intake (fruits, vegetables, whole grains)
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid straining during bowel movements
- Use warm sitz baths
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid long sitting hours
2.Medical Treatments
- Oral medications to reduce inflammation
- Ointments and suppositories
- Stool softeners
3.Minimally Invasive Procedures For advanced or persistent piles:
- Rubber band ligation
- Sclerotherapy
- Infrared coagulation (IRC)
4.Surgical Options
- Hemorrhoidectomy
- Stapler hemorrhoidopexy
- Laser piles surgery (modern, less painful option)
Prevention Tips
You can reduce the chances of developing piles by:
- Eating a balanced, high-fiber diet
- Staying hydrated
- Avoiding sitting on the toilet for long
- Exercising daily
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding heavy lifting
- Not ignoring the urge to pass stool
Conclusion
Piles are a common condition that can be uncomfortable but are highly treatable when addressed early. With proper care, lifestyle changes, and medical advice, most patients recover quickly without complications. If you notice persistent symptoms, consult a qualified specialist for timely diagnosis and treatment.